Your content might already rank well in Google, but what happens when users never click through? With AI Overviews, Bing Copilot, Perplexity, and chat-based search, answers are being generated instantly, and often without the need for a typical site visit. That shift means the old playbook of targeting blue links and optimizing for CTR doesn’t cut it anymore.
AI search engine optimization (AI SEO) is the next frontier. Instead of chasing positions, brands now compete for visibility inside summaries, citations, and answer boxes. This guide breaks down how AI SEO works, the strategies that matter most in 2025, and which metrics to track as you future-proof your search presence in our AI-first world.
AI search engine optimization is about making your content answer-ready for systems powered by large language models (LLMs). Instead of just aiming for the “10 blue links” on a results page, AI SEO helps your content show up inside AI Overviews, generative snippets, and even chat-based answers.
Think of how these engines work. First, they retrieve documents that look relevant. Then, the model generates a response by summarizing those documents — and, if you’re doing something right, citing the ones it trusts. That citation is the new click-through.
So, do keywords and backlinks still matter?
Yes.
Are they enough on their own?
Not quite.
To get cited, your content has to speak the same language as the machine. Entity-rich writing, clear definitions, structured data, and clean metadata. The easier you make it for a model to sift through your content, the more likely it is to select your content as a reliable source.
Structured data and content have always been one of the primary answers for how to optimize for search engines, so a lot of what you naturally do is already helping. So, traditional SEO isn’t dead. Fast load times, strong technical health, and mobile readiness are still table stakes. What’s changed is the layer on top: your brand now has to prove it’s a trusted authority for both humans and algorithms.
We always talk about Google, but that isn’t the only search engine or resource for results. They show up across an expanding ecosystem, including:
The message for marketers is clear: you’re not just optimizing for Google anymore. AI SEO means building content that can be selected, summarized, and cited across multiple surfaces — and more importantly, wherever your audience is asking questions.
Structure. Writing quality. Authority signals. That’s what large language models (LLMs) are looking for when deciding which content to trust. Instead of optimizing for a ranking, you’re optimizing for selection inside an AI-generated answer. That process leans on a few core elements:
When these pieces come together, your content becomes easier for AI to interpret, summarize, and cite. It shifts the goal from driving clicks to earning visibility inside the answers people already see. So, the more quote-ready your content is, the more visible your content and brand will be.
Traditional SEO rewarded visibility. AI SEO rewards credibility. Instead of just climbing search rankings, the goal is to become the source that AI systems trust enough to cite.
Getting to page one used to be the win. Now, the real prize is being quoted inside an AI Overview or chat result. That means structuring passages so they can be pulled directly into answers. For instance, a product comparison table or a one-sentence definition has a better shot of being cited than a long block of copy. Rankings still matter, but citations are what earn attention in AI search.
Stuffing in the right keyword variation won’t convince a model that your page is the best fit. What does? Entities and their relationships. Imagine writing about “running shoes.” Instead of just repeating the phrase, you’d define cushioning types, list popular brands, and connect those details to activities like marathon training or trail running. That context helps AI systems map how your content answers more specific queries.
Click-through rate once measured success, but if users get their answer from an AI summary, no click happens. AI share of voice tracks how often your brand is cited across Google AI Overviews, Bing Copilot, or Perplexity. For marketers, this metric reveals whether your expertise is showing up where people are now spending their attention: inside the generated response itself.
If your pages aren’t being cited in AI answers, they might as well be invisible. The fix isn’t complicated, but there are a couple of specifics you need to incorporate.

Think about how an AI model scans a page: it’s looking for clear, digestible chunks. Start sections with one-sentence definitions, then expand. Use lists, tables, and step-by-step breakdowns, formats that can be lifted directly into generated responses. Adding FAQs within a topic cluster also improves your odds of citation because the content is already shaped like an answer.
If you’re writing about “how to refinance a mortgage,” opening with a single-sentence definition followed by a step-by-step list gives the model exactly what it needs. FAQs work the same way—they mirror the Q&A style AI results are built on.

Schema is like a cheat sheet for machines — it provides the machine-readable signals AI models rely on. A recipe site using FAQPage, HowTo, Article, Product, Organization, and Person schema makes it far easier for AI to parse instructions, videos, and timings than one with plain text alone. The difference? One gets cited as a trusted source in a generated answer, the other is overlooked. Don’t just add markup, but test it with validation tools and keep metadata (author, date, org) clean.
Search engines still look for authority signals; AI just weighs them differently. Include expert bylines, clear author bios, and cite credible sources. Backlinks and third-party mentions reinforce authority beyond your own site. A medical site with content written by an MD, backed by references from the Mayo Clinic, is much more likely to be quoted than a generic health blog.
Featured snippets are often the training ground — and the live data source — for generative answers. Write concise answers at the top of a section, then elaborate. Use bullet lists for processes, definition tables for comparisons, and direct phrasing that AI can easily quote. If you run an e-commerce site, turning your “best laptops for students” blog into a bulleted comparison chart increases the odds of winning a snippet today and being cited in an AI Overview tomorrow.
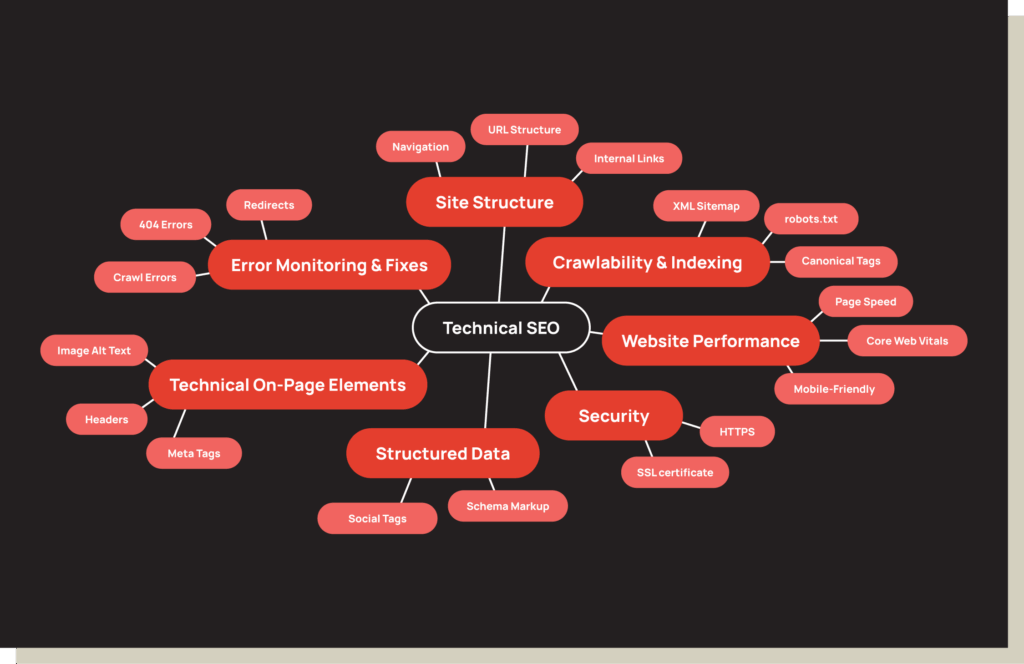
Even the best content gets skipped if it’s slow or messy, and AI search won’t cite a page that’s hard to access. Keep Core Web Vitals healthy, mobile UX smooth, and HTTPS standard. Maintain clean sitemaps and crawl budget hygiene so nothing gets missed. Don’t forget multimodal signals: alt text, transcripts, and captions increase the chance of your images, videos, or audio being pulled into AI responses.
Stale pages rarely get cited. Regularly update stats, examples, and dates to show relevance. Mark content with “last updated on” fields, and consolidate thin pages into authoritative hubs.
Take a cybersecurity blog that updates its “2023 phishing attack statistics” post with 2025 numbers. This signals relevance, while an outdated competitor page fades into the background. Adding “last updated” tags and consolidating thin content into a hub reinforces freshness, and that freshness helps your content stay visible when AI systems scan for the most current, reliable answers.
AI models cite what they can clearly identify. Use straightforward, factual phrasing. Reference reputable sources and include statements that stand on their own — short enough to be lifted directly into a generated summary. For example, writing “The average email open rate in 2025 is 21% (Statista)” gives AI a clean, source-backed fact it can lift directly. Compare that to burying the same stat inside a paragraph of fluff — harder to cite, easier to skip.
AI SEO relies on platforms that help with entity research, content optimization, technical checks, and — new to 2025 — tracking citations. Here’s where to focus when it comes to finding the right tools.
Tools like SEMrush Topic Research, Ahrefs Keywords Explorer, and AlsoAsked help uncover not just keywords, but the entities and questions AI models associate with them. For example, if you’re targeting “electric vehicles,” you’ll also see related entities like charging infrastructure, battery types, and federal tax credits — relationships you’ll want reflected in your content.
Platforms such as SurferSEO, Clearscope, and MarketMuse score your content against NLP models to highlight coverage gaps. Writing a guide on “remote team collaboration”? These tools surface semantically related phrases like project management software, asynchronous communication, and time zone overlap. This is how you make sure that your copy speaks the same language as AI search.
This is the newest tool category. New features from Sistrix, Ahrefs, and specialized platforms like Perplexity Pro Reports show how often your site is mentioned in AI Overviews, chat answers, or other generative surfaces. Instead of treating “AI share of voice” as an abstract idea, these tools quantify it.
Technical SEO underpins everything. Crawling and audit tools like Screaming Frog, OnCrawl, and Sitebulb keep Core Web Vitals, sitemaps, and log files clean, factors that directly influence whether AI systems can access and parse your content. Paired with ContentKing for continuous monitoring, you’ll know the moment a broken link, schema error, or slow load threatens your visibility.
For more context, Search Engine Journal’s roundup of AI SEO tools highlights how quickly this space is evolving.
Single pages being optimized are helpful, but you need them to come together with an entire optimized system, where every piece of content reinforces the rest. These three elements set that system up for success.
The hub-and-spoke model works especially well in AI search. A pillar page anchors the topic (say, “employee wellness programs”), while supporting articles dive into subtopics like fitness stipends, mental health benefits, or VTO policies. Interlinking signals topical authority and gives LLMs a clear map of how your content covers the space.
Think about outlines as blueprints for AI answers. Instead of writing a full draft and hoping it works for snippets later, design the structure up front. That might mean planning where a definition box goes, outlining a process as numbered steps, or slotting in a pros-and-cons table.
Treat expert input as a built-in stage of content design, not a final polish. Publishing with bylines, credentials, and references reinforces authority, but the real gain comes from weaving SME insights directly into the structure. That way, your content carries unique expertise that AI models can’t find in generic sources.
Click rates and rankings are still worth tracking, but when it comes to tracking AI SEO, there are some new (or reframed) metrics to monitor to see if your efforts are paying off.
Citation frequency is the new visibility metric. Track how often your site is referenced in Google AI Overviews, Bing Copilot, Perplexity, and other chat-based results. Some SEO platforms — Ahrefs among them — are rolling out features that quantify AI share of voice.
If you’re already tracking AI share of voice, the next step is to use that data strategically. Benchmark citation frequency against competitors to understand relative visibility, and watch for shifts in the types of queries where you’re cited. For example, an increase in citations around product-comparison queries might signal growing authority at the consideration stage of the funnel.
Organic metrics don’t disappear. Rankings, reach, impressions, and engagement still matter, especially when paired with assisted conversions and pipeline attribution. For example, if a product guide is cited in an AI Overview but also sees rising organic traffic and contributes to demo requests, you’ve got evidence that AI visibility is feeding the funnel, not just awareness.
AI search results evolve quickly, which means measurement has to be ongoing. Build quarterly checkpoints into your workflow: update schema, refresh content, and test snippet formats against key queries. A/B testing definitions, tables, or list structures can be especially helpful in determining what AI systems are most likely to pull into generated answers.
AI systems look for clear, scannable data when summarizing offerings. Product pages with benefits tables, comparison blocks, and FAQs are more likely to surface in AI Overviews.
One example comes from Princess Cruises, which needed to dominate Alaskan cruise searches. Instead of chasing keywords, they built topic clusters around their service pages: 70 new pieces of content, 23 optimized port landing pages, and a web of internal links pointing back to core pillars.
Within three months, this strategy drove a 261% increase in AI Overview mentions, capturing 66.2% of competitive mentions and 88.4% of impressions in AI-driven search. This 97th Floor case study shows how structuring content this way proves far more effective than traditional keyword targeting.
Guides and blog posts often answer early- or mid-funnel questions, which makes them prime candidates for AI answers. Starting with concise definitions, layering in structured summaries, and adding original charts or visuals helps these assets stand out. For example, a blog explaining “what is zero trust security” that opens with a crisp definition and includes a diagram will likely be favored over one with only dense paragraphs.
Glossaries and resource libraries are tailor-made for AI SEO. Short, canonical definitions backed by internal links to related topics create a knowledge graph effect that language models can navigate. For example, a glossary page might define an industry term in two or three sentences, then connect readers to deeper resources across your site. Even though the content is brief, its clarity and structure make it highly attractive for AI-generated summaries.
Optimizing for AI search raises new responsibilities. Accuracy and trustworthiness are even more important today to protect your brand. Here’s how to make sure your organization stays out of hot water.
Generative answers can spread errors if the sources feeding them are flawed. That makes it vital to maintain rigorous sourcing practices: cite reputable references, conduct boas checks, log updates, and monitor pages for outdated claims. Treat every page as if it could be quoted directly — because it might.
Generative AI has blurred the lines between original and machine-written material. To protect both your brand and your users, adopt clear policies on how AI is used in content creation. Human review and quality assurance should always be the last step before publishing. Where AI assistance is part of the process, disclosure fosters transparency and helps build trust.
Most teams start strong — refreshing content, adding schema, tracking AI citations. But if traffic plateaus, citations remain sparse, or entity coverage feels incomplete, it may signal the limits of internal bandwidth. What works this quarter may look different six months from now, and the brands winning citations are the ones adapting fastest. We can help with that.
We’ve built systems that scale with change: topic clusters that expand as industries shift, schema frameworks that grow with new content types, and measurement models that capture how AI surfaces your brand across platforms. The result is momentum, increasing visibility that keeps clients ahead while competitors scramble to catch up.
If your goal is to lead in an AI-first search landscape, our team has the playbook and the proof to make it happen. Let’s talk.
Traditional SEO aimed at rankings; AI SEO focuses on being selected and cited in generated answers. The difference is speed of change—LLMs update constantly, so winning visibility requires ongoing adaptability, not an outdated optimization checklist.
Look for tools that track AI citations, model entities, and highlight semantic gaps. Platforms that combine technical monitoring with content optimization provide the clearest picture of how your site is being surfaced across generative search engines.
Write extractable content (short definitions, lists, and structured tables) backed by strong authority signals. Google favors sources that are both clear and trustworthy, so freshness, schema, and citations from reputable outlets all increase citation odds.
AI citations matter, but they’re only part of the story. Combine citation frequency with down-funnel metrics like influenced conversions, pipeline contribution, or demo requests to show that AI visibility is driving measurable business outcomes.
It can surface temporarily, but lasting visibility should be left to good old human oversight. Content reviewed and enriched by subject-matter experts builds credibility that LLMs recognize, so it’s far more likely to sustain citations over time.
Yes. Schema is a machine’s shortcut to understanding. Start with FAQPage, Article, and Organization markup. Then expand into page-specific types like Product, VideoObject, or HowTo as you scale.
If your content is plateauing, AI citations are low, or entity coverage feels incomplete, it may be time to bring in specialists. Agencies offer the technical depth and content frameworks needed to compete at scale.

